Backup Harness in Git using Git Experience and Terraform
Harness Continuous Delivery (CD) has evolved to seamlessly integrate with modern DevOps tools, notably Git and Terraform. This article will guide you through backing up your Harness CD configurations to GitHub using the Harness Git Experience and Harness Terraform Provider.
To learn more, go to:
Harness Git Experience Setup
Harness Git Experience allows you to treat your CD configurations as code stored in a Git repository. When integrated with GitHub, every change made in the Harness platform can be version-controlled in a GitHub repository. In addition, with bidirectional sync enabled, you can have Git Experience sync two-way (bidirectionally) between Harness and your Git repo.
Harness Git Experience supports the following key entities:
- Pipeline
- Templates
- Input Sets
- Governance Policies
To set up Harness Git Experience for backups, do the following:
-
Create a GitHub repository: If you haven't already, set up a dedicated repository in GitHub for your Harness configurations.
-
Connect Harness with GitHub:
- Please follow the steps in the Harness Git Experience quickstart.
-
Sync configurations with GitHub:
- In Harness, enable Git Experience for your entities.
- Specify the GitHub repository, branch, and file paths for synchronization.
By navigating to your account/project settings, you can enforce that all Harness project pipelines, templates, and input sets are backed up in GitHub.
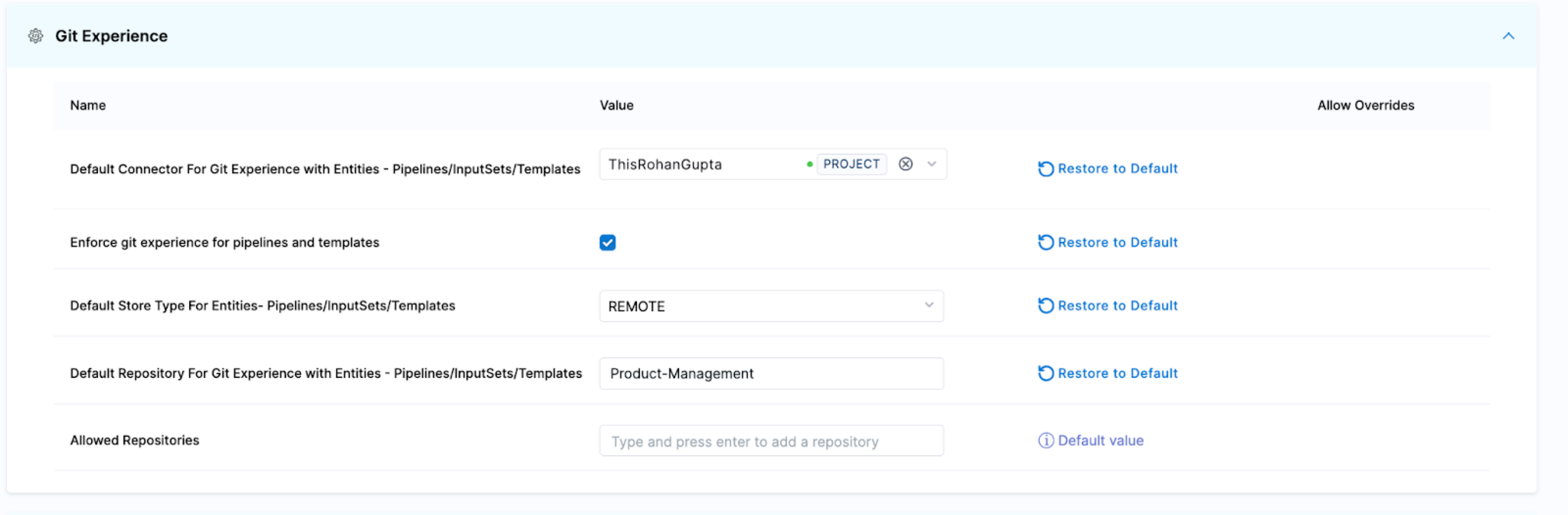
You can organize the repo to look like this:
├── Pipeline
│ ├── dev_pipeline.yaml
│ ├── qa_pipeline.yaml
│ ├── prod_pipeline.yaml
├── Templates
│ ├── Step_Templates
│ │ ├── bash_job_step.yaml
│ ├── Stage_Templates
| | |-- deploy_stage.yaml
│ ├── Piprline_Templates
│ ├── Step_Group_Templates
├── Input Sets
| |- Prod_Inputs.yaml
└── .gitignore
Harness Terraform Provider Setup
The Harness Terraform Provider takes backup further by allowing you to define and manage Harness resources using Terraform. This enables an Infrastructure as Code (IaC) approach.
You can manage the other Harness resources like connectors, secrets, projects, etc., via the Terraform Provider.
Using this approach requires you to manage all resources and onboarding via Terraform. This is to ensure that the Terraform state file is the same as the Harness state.
To set up the Harness Terraform Provider for backups, do the following:
-
Install the Harness Terraform Provider: Add the Harness provider to your Terraform configuration. For more information, go to the Terraform Provider docs.
terraform {
required_providers {
harness = {
source = "harness/harness"
version = "0.28.2"
}
}
}
provider "harness" {
# Configuration options
} -
Define Harness Resources: Write Terraform configurations that describe your Harness resources. For instance, you can define an application in Harness as:
resource "harness_platform_pipeline" "example" {
identifier = "identifier"
org_id = "orgIdentifier"
project_id = "projectIdentifier"
name = "name"
git_details {
branch_name = "branchName"
commit_message = "commitMessage"
file_path = "filePath"
connector_ref = "connectorRef"
store_type = "REMOTE"
repo_name = "repoName"
}
yaml = <<-EOT
pipeline:
name: name
identifier: identifier
allowStageExecutions: false
projectIdentifier: projectIdentifier
orgIdentifier: orgIdentifier
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: dep
identifier: dep
description: ""
type: Deployment
spec:
serviceConfig:
serviceRef: service
serviceDefinition:
type: Kubernetes
spec:
variables: []
infrastructure:
environmentRef: testenv
infrastructureDefinition:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: testconf
namespace: test
releaseName: release-<+INFRA_KEY>
allowSimultaneousDeployments: false
execution:
steps:
- stepGroup:
name: Canary Deployment
identifier: canaryDepoyment
steps:
- step:
name: Canary Deployment
identifier: canaryDeployment
type: K8sCanaryDeploy
timeout: 10m
spec:
instanceSelection:
type: Count
spec:
count: 1
skipDryRun: false
- step:
name: Canary Delete
identifier: canaryDelete
type: K8sCanaryDelete
timeout: 10m
spec: {}
rollbackSteps:
- step:
name: Canary Delete
identifier: rollbackCanaryDelete
type: K8sCanaryDelete
timeout: 10m
spec: {}
- stepGroup:
name: Primary Deployment
identifier: primaryDepoyment
steps:
- step:
name: Rolling Deployment
identifier: rollingDeployment
type: K8sRollingDeploy
timeout: 10m
spec:
skipDryRun: false
rollbackSteps:
- step:
name: Rolling Rollback
identifier: rollingRollback
type: K8sRollingRollback
timeout: 10m
spec: {}
rollbackSteps: []
tags: {}
failureStrategies:
- onFailure:
errors:
- AllErrors
action:
type: StageRollback
EOT
}
-
Version control with GitHub: Push your Terraform configurations to your GitHub repository. Any change in the configurations can be tracked via git commits, pull requests, and more.
Here's an example repo setup:
├── project
| |-- connectors
│ | ├── connetor_k8s.tf
│ | |── connector_github.tf
│ | |── connector_docker.tf
| |--- secrets
│ ├── ssh_secret_text
│ │ ├── git_secret.tf
│ ├── ssh_key
| | |-- deploy_key.tf
│ ├──
│ ├── pipelines
├ |--templates
| |- servies
| |- environments
| |- infrastructure_definition
└── project.tf
For more information follow our Solutions Architecture Team’s repo.
Conclusion
Using a combination of Harness Git Experience and the Harness Terraform Provider, you can successfully back up your projects and resources and restore what was potentially lost.
We recommend using the Git Experience to back up and save pipelines, templates, input sets, and policies.
You can use the Terraform Provider to manage services, environments, connectors and infrastructure definitions in Harness.
Harness CD integration with tools like Git and Terraform empowers DevOps teams to manage and back up configurations with efficiency and precision. By leveraging GitHub and the Harness Terraform Provider, you can adopt a robust version control and IaC strategy, ensuring that your CD processes are resilient, traceable, and restorable.